
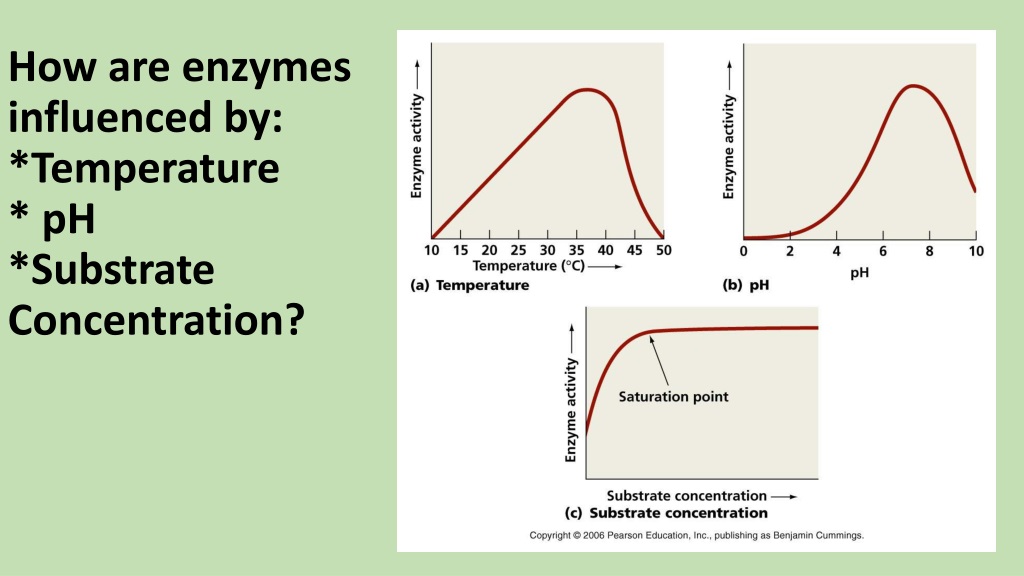

What is a catalyst? It is a substance that enables a reaction to occur faster, using less energy. Enzymeĭirections: Watch Enzymes in Action: How Apples Turn Brown to see an example of how enzymes work.European explorers had adequate knowledge, skills and equipment, but why didn't they reach the New World until the end of the 15th century? You'll be surprised to learn that the answer to this question is related to the small biological molecules called enzymes, that act as catalysts. Below is a chart of some more common enzymes and the substrates they act upon. For example, the enzyme that breaks down the sugar sucrose is called sucrase. What do you notice about all the enzymes in the list above? With few exceptions, the names of enzymes end in "-ase." The name depends on their role in the metabolic process and the substrate they interact with. Cellulases are the reason cows and termites are able to digest things like grass and wood. Bacteria in the guts of cows and termites excrete cellulases. Cellulases: Cellulases break cellulose molecules down into simpler sugars.Your saliva contains amylase, and so does your small intestine. Amylases: Amylases break down starch chains into smaller sugar molecules.Proteases (also called peptidases): A protease is any enzyme that can break down a long protein into smaller chains called peptides.Some enzymes you may have heard of include the following: coli bacteria excrete enzymes to break down food in their environment into molecules small enough to pass through the cell wall and into the cell. Some cells also excrete enzymes outside of their cell walls to break down molecules in the environment. How does substrate concentration affect the action of enzymes?Ĭells use enzymes to catalyze a variety of reactions internally, including reactions involved in growth, reproduction, digestion, and nutrient absorption. How does pH affect the action of enzymes? How does temperature affect the action of enzymes? How do enzymes work to speed up chemical reactions?

The student is expected to:ī(9)(C) identify and investigate the role of enzymesĭescribe the role enzymes play in biological systems.Įxplain how enzymes work to speed up chemical reactions.Įxplain how enzyme structure determines enzyme specificity.ĭesign and conduct experiments and interpret the data obtained to draw conclusions about how various factors affect enzyme activity. Before you get started, don’t forget to print out your OnTRACK Biology Journal.ī(9) The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms. Let’s learn about what enzymes are and how they work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
